Information
Jul 18, 2023
Challenging Radiology Diagnostic Quizzes vs ChatGPT: Verification of Diagnostic Accuracy Using GPT-4
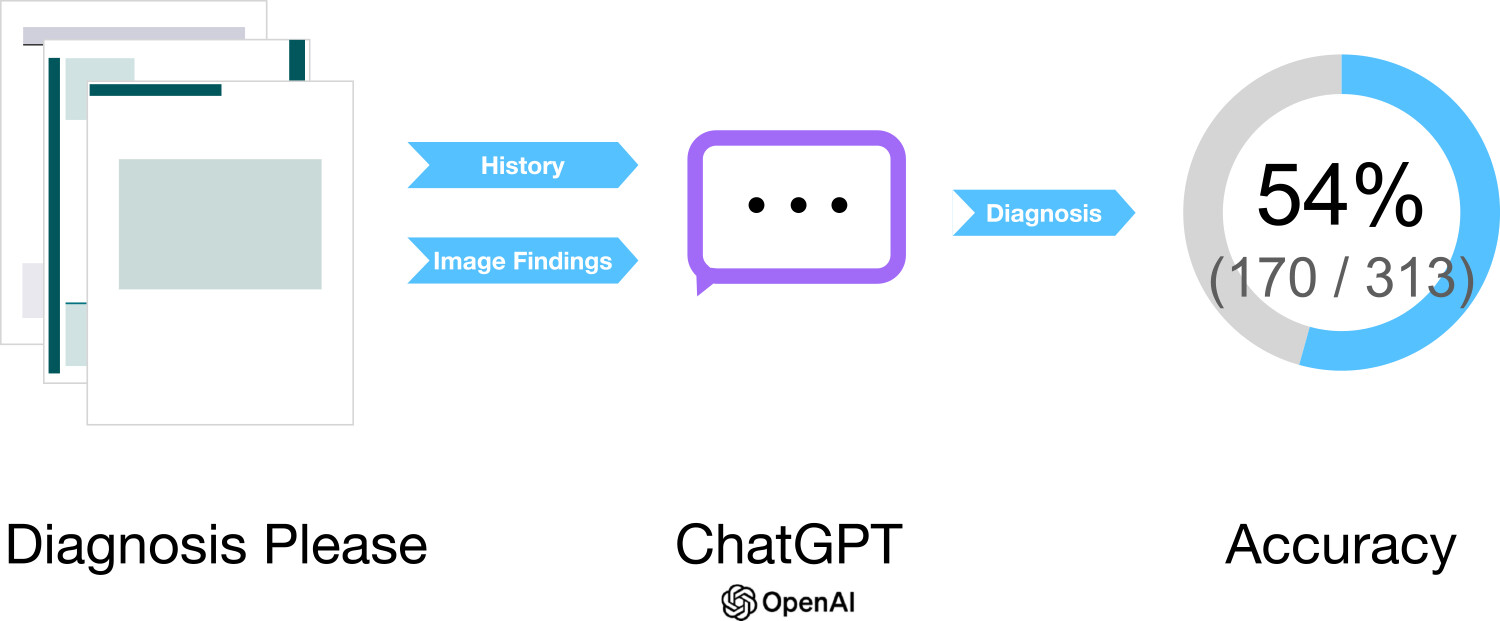
We revealed that ChatGPT powered by the large language model GPT-4 demonstrated approximately 54% accuracy on "Diagnosis Please" quizzes.
Paper
Diagnostic Performance of ChatGPT from Patient History and Imaging Findings on the Diagnosis Please Quizzes
Radiology
https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.231040
Author's Comments
Shortly after GPT-4 was introduced to ChatGPT, we were impressed by the technology and decided to complete this research quickly. While validations using large language models in the medical field have increased recently, compiling this paper during what could be considered the early stages was an exciting experience. Additionally, we communicated extensively with Radiology's editorial committee to improve how our work was disseminated to our colleagues. Initially submitted as an original paper, we ultimately agreed to convert it to a short article, which I believe was possible because they responded positively, saying they could feel our passion during our exchanges. The enlightening discussions we had with the editorial committee during the submission process strengthened our commitment to our research.
Paper Overview
This paper investigates how accurately GPT-4-based ChatGPT can derive final diagnoses for the "Diagnosis Please" quizzes regularly published in Radiology. Patient history and medical imaging findings, which are important information sources in clinical practice, were provided incrementally for diagnosis. Since ChatGPT itself cannot directly interpret images, we presented findings extracted from the papers as text, and two radiologists evaluated the results. Among 313 cases, the accuracy rate was 22% when diagnosis was based solely on patient history, but improved to 57% when diagnosis was based solely on imaging findings, and reached 61% when both were combined. For the task of determining a single definitive diagnosis, an overall accuracy rate of 54% was demonstrated.
Paper Details
This study examined 313 cases published from 1998 to 2023, having ChatGPT provide differential diagnoses at three stages for each quiz: based on "patient history," "presented imaging findings," and "combined information." Subsequently, ChatGPT was asked to select a final diagnosis, which was then evaluated for agreement with the correct answer published in Radiology. Considering the possibility that cases from before September 2021 might have been included in the training data, this represents more solid performance than anticipated. We did confirm that there was no statistically significant difference in performance between the pre and post GPT-4 training time periods. Notable differences appeared across clinical domains, with cardiovascular cases showing a high accuracy of 79%, while musculoskeletal cases had an accuracy of 42%. When specialists evaluated the appropriateness of differential diagnoses provided by ChatGPT on a 5-point scale, the median reached 5.0, indicating generally satisfactory results. However, this quiz format has more constraints compared to actual clinical environments, and this verson of ChatGPT also had the weakness of being unable to directly reference images. Nevertheless, amid concerns about radiologist shortages, demonstrating the potential for such AI-based immediate decision support is meaningful. Ultimately, we confirmed ChatGPT's moderate reliability, though it's not uniformly effective across all clinical domains, and we recognize the need for further validation in the future.