Information
Jun 24, 2024
Examining Medical AI and Climate Change: Considerations for a Sustainable Future
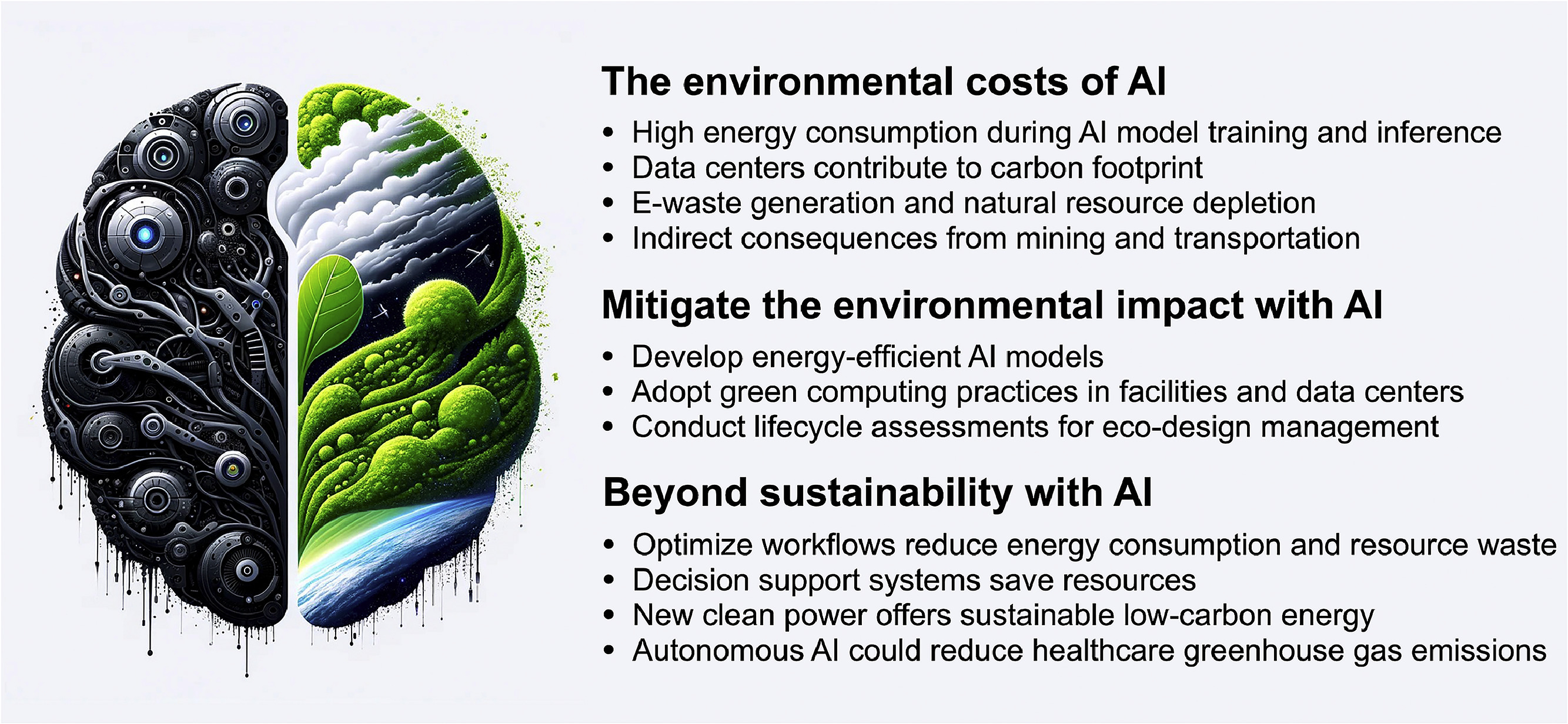
This is a review that organizes challenges and countermeasures from both perspectives: the advancement of healthcare brought by AI technology and the increasing environmental burden behind it.
Paper
Climate change and artificial intelligence in healthcare: Review and recommendations towards a sustainable future
Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2024.06.002
Author's Comments
We focused on the fact that while AI use in medical settings is rapidly expanding, it also creates a significant environmental burden due to its dependence on computing resources. Recently, advanced AI such as large language models (LLMs) have been attracting attention, but the computational resources and power consumption of the data centers they use are greater than we imagine, and their impact on climate change can no longer be ignored. Therefore, in cooperation with medical AI stakeholders throughout Japan, we compiled this review to simultaneously consider the social responsibilities of healthcare and the global challenge of climate change. Our laboratory has established Planetary Health as a major theme, and we believe this paper will serve as a useful starting point for exploring the compatibility between the global environment and healthcare.
Paper Overview
This paper comprehensively discusses both the diagnostic and treatment benefits of medical AI, as well as its environmental impact, including greenhouse gas emissions from energy-intensive model training and data center operations. While the healthcare sector as a whole reportedly accounts for about 4.4% of global greenhouse gas emissions, AI use is predicted to expand further. Therefore, we conclude that specific mitigation measures, such as power-saving technologies in the AI development stage and the introduction of renewable energy, are essential. Additionally, through collaborative research with multiple experts, we propose the need for more responsible AI implementation and policies that consider environmental impact.
Paper Details
This review first demonstrates the specific burden that AI systems place on the environment. Based on current estimates, training a single large AI model produces emissions equivalent to the lifetime emissions of five passenger cars (Strubell et al., 2019) and constant parts upgrades increases the problem of electronic waste (e-waste). We point out that this issue cannot be avoided in the medical field either. We show that while data centers account for about 1% of global power consumption, a certain amount of reduction can be expected through the use of renewable energy and efficient hardware selection. Furthermore, we organized from multiple reports indicating the possibility that proper utilization of AI could reduce waste in medical services themselves, potentially contributing to a reduction of up to 80% in greenhouse gas emissions. To support these efforts, it is necessary to be conscious of lifecycle assessment from the research and development stage and to comprehensively consider environmental factors ranging from medical equipment disposal to material procurement. fulfill its social responsibility and leave both a healthy planet and healthcare system to the next generation.