Research Results
Aug 20, 2016
- Press Release
- Research Paper
A press release announcing the research findings of Prof. Yutaka Amao's group has been issued
A novel molecule has been synthesized that exhibits a 560-fold increase in catalytic activity for the conversion of carbon dioxide to formic acid.

This research presentation was introduced in the following media.
- 8/23 The Chemical Daily
- 8/25 The Asahi Shimbun
- 9/5 The Nikkei
Professor Yutaka Amao (Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis) and Graduate Student Shusaku Ikeyama ( Graduate School of Science Doctoral Program) have synthesized a novel artificial coenzyme that exhibits a 560-fold increase in catalytic activity for the conversion of carbon dioxide to formic acid when compared to natural coenzymes.
Research Summary
The development of efficient catalysts is a critical component in constructing an artificial photosynthesis system that harnesses solar energy to transform carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
In this study, we have successfully developed a simple artificial coenzyme that dramatically improves the catalytic activity of formate dehydrogenase, an enzyme that accelerates the conversion of carbon dioxide into formic acid, which can be used as a fuel, chemical, or energy storage medium.
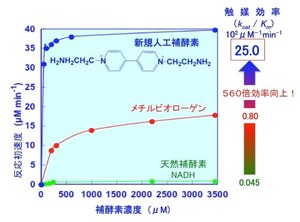
The catalytic conversion of carbon dioxide into formic acid by formate dehydrogenase is dependent on the presence of a coenzyme. Previous research has demonstrated that the employment of artificial coenzymes, specifically methyl viologen*1 and diquat*2, in conjunction with formate dehydrogenase, results in a substantial increase in catalytic activity when compared to the utilization of natural coenzymes.
*1: http://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/ja/news/2015/81sxi
*2: http://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/ja/news/2016/160805
By introducing two amino groups (-NH2) into the viologen chemical structure, we synthesized a novel compound and utilized it as an artificial coenzyme. This modification led to a significant enhancement in catalytic activity, achieving a 560-fold increase compared to the maximum activity obtained with natural coenzymes in previous studies.
Our findings are anticipated to make substantial contributions to the design and development of catalysts employed in artificial photosynthesis systems, aiming to convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds.
Publication Information
| Publications: | Chemistry Letters |
|---|---|
| Title of Paper: | Novel artificial co-enzyme based on the viologen derivative for CO2 reduction biocatalyst formate dehydrogenase |
| Author: | Shusaku Ikeyama and Yutaka Amao |
| URL: | http://www.journal.csj.jp/toc/cl/0/0 *1 : This paper will be published in advance as an Advance Publication, unproofed. |